문제 이미지
1차 풀이
최적화 풀이 혹은 살짝 방법만 다른 2차 풀이법
순서입니다

// Ex01
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("현재몸무게를 입력하세요 : ");
int weight = sc.nextInt();
System.out.print("목표몸무게를 입력하세요 : ");
int goal = sc.nextInt();
int week =1;
while (weight > goal) {
System.out.print(week+"주차 감량 몸무게 : ");
int lose = sc.nextInt();
week++;
weight -= lose;
}
System.out.println(weight+"kg 달성!! 축하합니다!");

// Ex02
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("일한 시간을 입력하세요 : ");
int workTime = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println(workTime>8 ? "총 임금은 "+((workTime-8)*7500+40000)+"원 입니다"
: "총 임금은 "+workTime*5000+"원 입니다" );

// Ex03
int n=1;
int sum=0;
while(n<100) {
System.out.print(n+" ");
sum+=n;
if(n>0) {
n++;
}else n--;
n*=(-1);
}
System.out.println(" ");
System.out.println("결과 : "+sum);

// Ex04
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("총금액 입력 : ");
int change = sc.nextInt();
int a = change/10000;
int a2 = change%10000;
int b = a2/5000;
int b2 = a2%5000;
int c = b2/1000;
int c2 = b2%1000;
int d = c2/500;
int d2 = c2%500;
int e = d2/100;
int e2 = d2%100;
System.out.println(" ");
System.out.println("잔돈 : "+change+"원");
System.out.println("10000원 : "+a+"개");
System.out.println("5000원 : "+b+"개");
System.out.println("1000원 : "+c+"개");
System.out.println("500원 : "+d+"개");
System.out.println("100원 : "+e+"개");

// Ex05
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("행 개수 : ");
int line = sc.nextInt();
for(int i=0; i<line; i++) {
for(int j=0; j<i+1; j++) {
System.out.print("*");
}
System.out.println();
}

// Ex06
int a = 77;
int b = 1;
int result = 0;
int sum=0;
while (a>0) {
result = a*b;
sum+=result;
a--;
b++;
}
System.out.println(sum);

// Ex07
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("행 개수 : ");
int line = sc.nextInt();
for(int i=0; i<line; i++) {
for(int j=line-i; j>0; j--) {
System.out.print("*");
}
System.out.println();
}

// Ex08
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("A 입력 >> ");
int a = sc.nextInt();
System.out.print("B 입력 >> ");
int b = sc.nextInt();
int result = (a-b);
while(a!=0 || b!=0) {
System.out.println("결과 >> "+result);
System.out.print("A 입력 >> ");
a = sc.nextInt();
System.out.print("B 입력 >> ");
b = sc.nextInt();
result = (a-b);
}
System.out.println("프로그램 종료");

// Ex09
// 정수를 입력받아 1의 자리에서 반올림 한 결과 출력
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("숫자 입력 : ");
int num = sc.nextInt();
int tail = num%10;
if(tail<5) {
System.out.println("반올림 수 : "+(num-tail));
}else if(tail>=5) {
System.out.println("반올림 수 : "+(num-tail+10));
}

// Ex10
for (char c = 'A'; c <= 'Z'; c++) {
System.out.print(c + " ");
}
// char 의 특성 고려
👽
// Ex11
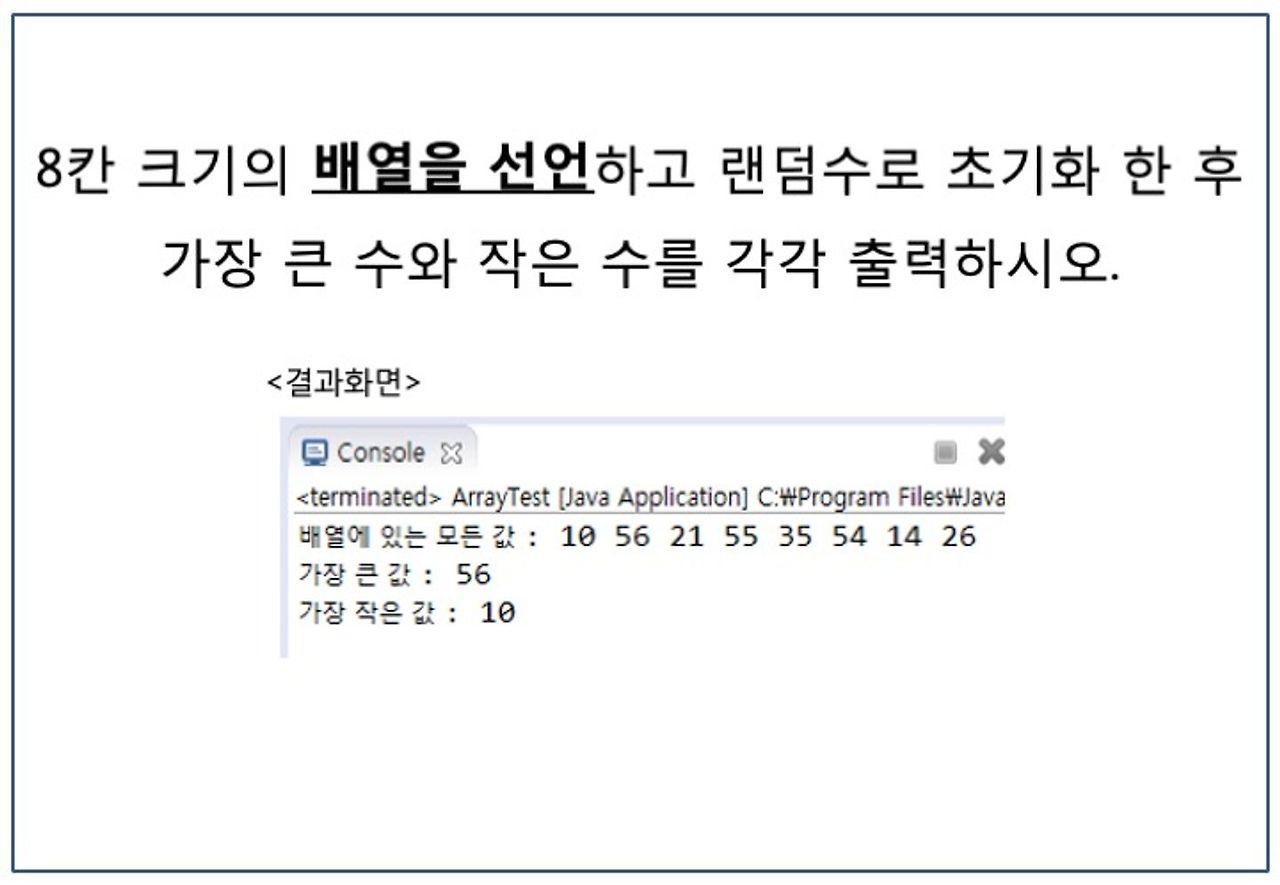
// int [8]의 랜덤 수를 지정하고 최댓값과 최솟값 출력
Random ran = new Random();
int[] num = new int[8];
int max = 0;
int min = 100;
for (int i=0; i<num.length; i++) {
num[i] = ran.nextInt(99)+1;
}
System.out.print("배열에 있는 모든 값 : ");
for(int i=0; i<num.length; i++) {
System.out.print(num[i]+" ");
}
for(int i=0; i<num.length; i++) {
if(num[i]>max) {
max = num[i];
}
if(num[i]<min) {
min = num[i];
}
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("가장 큰 수 : "+max);
System.out.println("가장 작은 수 : "+min);

👽
// Ex12
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num1 = 10;
int num2 = 2;
boolean result = isDivide(num1, num2);
System.out.println("결과 확인 : "+result);
}
private static boolean isDivide(int num1, int num2) {
boolean div = (num1%num2==0 ? true : false);
return div;
}

// Ex13
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("정수를 입력하세요 : ");
int num = sc.nextInt();
int[][] array = new int[num][num];
int a=1;
for(int i=0; i<array.length; i++) {
for(int j=0; j<array[i].length; j++) {
array[i][j]=a;
a++;
}
}
for(int i=0; i<array.length; i++) {
for(int j=0; j<array.length; j++) {
System.out.print(array[j][i]+"\t");
}
System.out.println();
}

// Ex14
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(getMiddle("power"));
System.out.println(getMiddle("test"));
}
public static String getMiddle(String word) {
int length = word.length();
int middle = length / 2;
if (length % 2 == 0) {
return word.substring(middle - 1, middle + 1);
}else{
return word.substring(middle, middle + 1);
}
}
// Ex14
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(getMiddle("power"));
}
private static String getMiddle(String str) {
String[] array = str.split("");
if(array.length%2==0) {
return array[(array.length/2)-1]+array[array.length/2];
}else {
return array[array.length/2];
}
}

// Ex15
String score = "A,A,B,C,D,A,C,D,D,D,F";
String[] scores = score.split(",");
int countA = 0;
int countB = 0;
int countC = 0;
int countD = 0;
int countF = 0;
for (String s : scores) {
switch (s) {
case "A":
countA++;
break;
case "B":
countB++;
break;
case "C":
countC++;
break;
case "D":
countD++;
break;
case "F":
countF++;
break;
}
}
System.out.println("A: " + countA + "명");
System.out.println("B: " + countB + "명");
System.out.println("C: " + countC + "명");
System.out.println("D: " + countD + "명");
System.out.println("F: " + countF + "명");
// Ex15
String score = "A,A,B,C,D,A,C,D,D,D,F";
int[] gradeCounts = new int[128];
for (char grade : score.toCharArray()) {
gradeCounts[grade]++;
}// toCharArray 는 문자열을 문자배열로 변환시킬때 사용
for (char grade = 'A'; grade <= 'F'; grade++) {
System.out.println(grade + ": " + gradeCounts[grade] + "명");
}

👽
// Ex16
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("정수를 입력하세요 : ");
int num = sc.nextInt();
int[][] array = new int[num][num];
int a = 1;
for(int i=0; i<array.length; i++) {
for(int j=0; j<array.length; j++) {
array[i][j]=a;
a++;
}
}
for(int i=0; i<array.length; i++) {
for(int j=0; j<array.length; j++) {
System.out.print(array[i][j]+"\t");
}
System.out.println();
}

// Ex17
// 생각을 잘못하면 어려울 수 있지만
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("정수를 입력하세요 : ");
int n = sc.nextInt();
int[] array = new int[n];
int sum = 1;
for(int i=0; i<array.length; i++) {
array[i] = sum+i;
sum+=i;
}
for(int i=0; i<array.length; i++) {
System.out.print(array[i]+" ");
}

👽
// Ex18
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("정수 입력(8자리) : ");
int num = sc.nextInt();
int sum = 0;
for(int i=0; i<8; i++) {
int a = num%10;
sum+=a;
num/=10;
}
System.out.println("합은 "+sum+"입니다");

// Ex19
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num1 = 50;
int num2 = 15;
char op = '*';
System.out.print(cal(num1, num2, op));
}
private static int cal(int num1, int num2, char op) {
int result = 0;
if(op=='-') {
result = num1-num2;
}else if(op=='+') {
result = num1+num2;
}else if(op=='*') {
result = num1*num2;
}else if(op=='/') {
result = num1/num2;
}
return result;
}

👽
// Ex20
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int[] array = new int[10];
for(int i=1; i<11; i++) {
System.out.print(i+"번째 정수 입력 >> ");
int num = sc.nextInt();
if(num%3==0) {
array[i-1]=num;
}
}
System.out.print("3의 배수 : ");
for(int i=0; i<array.length; i++) {
if(array[i]!=0) {
System.out.print(array[i]+" ");
}
}

👽
// Ex21
Random ran = new Random();
int lucky = ran.nextInt(100)+1;
int[] array = new int[6];
for(int i=0; i<array.length; i++) {
array[i] = ran.nextInt(10)+1;
for(int j=0; j<i; j++) {
if(array[i]==array[j]) {
i--;
}
}
}
for(int x:array) {
System.out.println("행운의 숫자 : "+x);
}

👽
// Ex22
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int[] array = new int[5];
for(int i=0; i<5; i++) {
System.out.print(i+"번째 별의 수 : ");
int num = sc.nextInt();
array[i] = num;
}
for(int i=0; i<array.length; i++) {
System.out.print(array[i]+" : ");
for(int j=0; j<array[i]; j++) {
System.out.print("*");
}
System.out.println();
}

// Ex23
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("단 입력 : ");
int a = sc.nextInt();
System.out.print("숫자 입력 : ");
int b = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println(a+"단");
for(int i=1; i<b+1; i++) {
System.out.println(a+"*"+i+"="+a*i);
}

// Ex24
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("숫자 입력 : ");
int num = sc.nextInt();
// 1 2 4 8 16
// 0 1 2 4 8
int a = num;
int n = 0;
int[] array = new int[num];
for(int i=0; i<array.length; i++) {
array[i]=2;
}
while(a!=0) {
array[n] = a%2;
a/=2;
n++;
}
for(int i=n-1; i>=0; i--) {
if(array[i]!=2) {
System.out.print(array[i]+" ");
}
}
// Ex24
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("10진수 정수를 입력하세요: ");
int num = sc.nextInt();
String binary = Integer.toBinaryString(num);
// Integer.toBinaryString() 10진수 정수를 2진수 문자열로 변환하는 내장 메소드
System.out.println("2진수로 변환한 결과: " + binary);
}
}

// Ex25
int[] point = { 92, 32, 62, 9, 81, 2, 68 };
int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int position1 = 0;
int position2 = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < point.length - 1; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < point.length; j++) {
int distance = (point[i] >= point[j]) ? point[i] - point[j] : point[j] - point[i]; // 두 숫자의 거리 계산
if (distance < min) {
min = distance;
position1 = i;
position2 = j;
}
}
}
System.out.println("가장 가까운 두 숫자의 위치: " + position1 + ", " + position2);

👽
// Ex26
for(int i=1; i<=5; i++) {
for(int j=5-i; j>0; j--) {
System.out.print(" ");
}
for(int j=1; j<i+1; j++) {
System.out.print("*");
}
System.out.println();
}

👽
// Ex27
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int[] array = new int[5];
for (int i = 1; i < 6; i++) {
System.out.print(i + "번째 수 입력 : ");
array[i - 1] = sc.nextInt();
}
for (int i = 0; i < array.length - 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < array.length - i - 1; j++) {
if (array[j] > array[j + 1]) {
int n = array[j];
array[j] = array[j + 1];
array[j + 1] = n;
}
}
}
System.out.println("정렬 후");
for (int x : array) {
System.out.print(x + " ");
}

// Ex28
int[][] array = new int[5][5];
int n = 1;
for(int i=0; i<array.length; i++) {
for(int j=0; j<array[i].length; j++) {
array[i][j] = n;
n++;
}
}
System.out.println("원본");
for(int i=0; i<array.length; i++) {
for(int j=0; j<array[i].length; j++) {
System.out.print(array[i][j]+"\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println("90도 회전");
for(int i=array.length-1; i>=0; i--) {
for(int j=0; j<array[i].length; j++) {
System.out.print(array[j][i]+"\t");
}
System.out.println();
}

// Ex29
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("N 입력 : ");
int n = sc.nextInt();
System.out.print("X 입력 : ");
int x = sc.nextInt();
int[] array = new int[n];
for(int i=0; i<n; i++) {
System.out.print((i+1)+"번째 정수 입력 : ");
int a = sc.nextInt();
if(a<x) {
array[i]=a;
}else array[i]=0;
}
System.out.print("결과 : ");
for(int i=0; i<array.length; i++) {
if(array[i]!=0) {
System.out.print(array[i]+" ");
}
}

// Ex30
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("첫자리 0을 제외한 숫자를 입력해주세요 : ");
int num = sc.nextInt();
int sum = 0;
int a = 0;
while(num!=0){
a = num%10;
if(a==1) {
sum+=2;
}else if(a==7) {
sum+=3;
}else if(a==4) {
sum+=4;
}else if(a==2 || a==3 || a==5) {
sum+=5;
}else if(a==0 || a==6 || a==9) {
sum+=6;
}else sum+=7;
num/=10;
}
System.out.println("대시('-')의 총합 : "+sum);
배열을 사용할 수 있긴한데 거기서거기인거같음
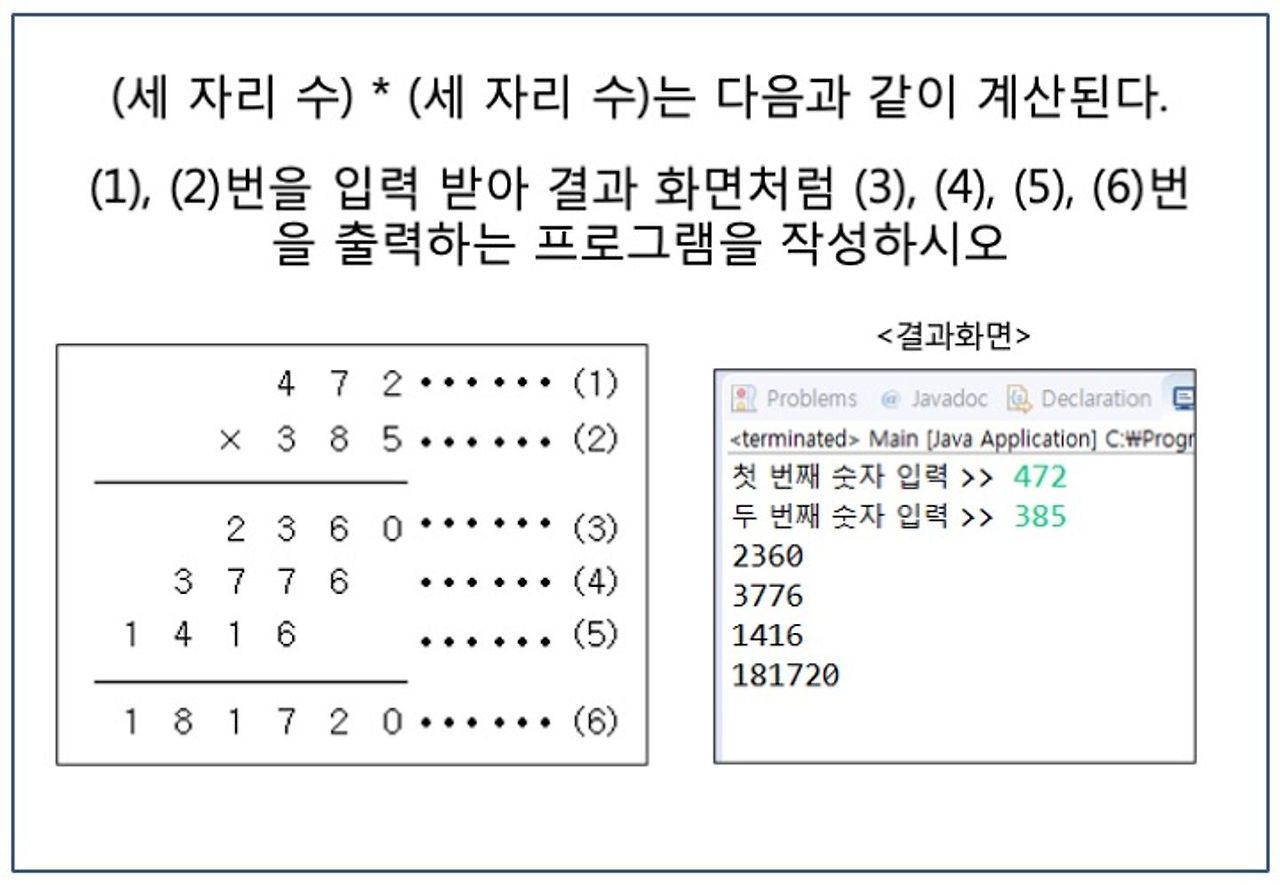
// Ex31
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("첫 번째 숫자 입력 : ");
int num1 = sc.nextInt();
System.out.print("두 번째 숫자 입력 : ");
int num2 = sc.nextInt();
int[] array = new int[4];
int a=num2;
for(int i=0; i<3; i++) {
array[i] = num1*(a%10);
a/=10;
}
array[3] = num1*num2;
for(int x:array) {
System.out.println(x);
}
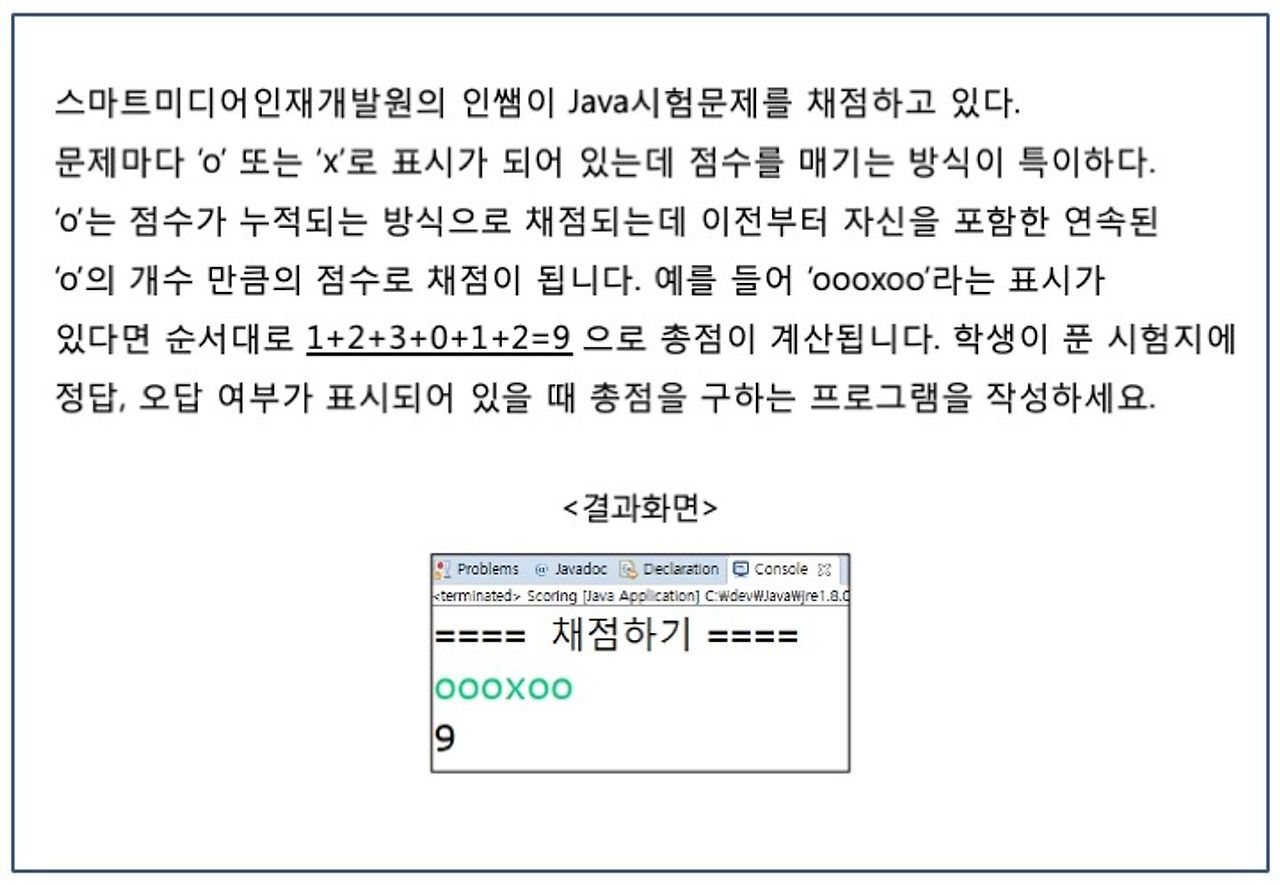
// Ex32
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("==== 채점하기 ====");
String input = sc.next();
int score = 0;
int correct = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < input.length(); i++) {
char c = input.charAt(i);
if (c == 'o') {
correct++;
score += correct;
} else if (c == 'x') {
correct = 0;
} else {
System.out.println("올바른 입력이 아닙니다. o 또는 x로 입력하세요.");
return;
}
}
System.out.println("총점: " + score);
// Ex32
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("==== 채점하기 ====");
String input = sc.next();
String[] array = input.split("");
int score = 0;
int correct = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
if (array[i].equals("o")) {
correct++;
score += correct;
} else if (array[i].equals("x")) {
correct = 0;
} else {
System.out.println("올바른 입력이 아닙니다. o 또는 x로 입력하세요.");
}
}
System.out.println("총점: " + score);
👽
// Ex33
public static void main(String[] args) {
int base = 10;
int n = 2;
int result = powerN(base, n);
System.out.println("결과 확인 : "+result);
}
private static int powerN(int base, int n) {
int result=1;
for(int i=0; i<n; i++) {
result*=base;
}
return result;
}
// Ex33
public static void main(String[] args) {
int base = 10;
int n = 2;
int result = powerN(base, n);
System.out.println("결과 확인 : "+result);
}
private static int powerN(int base, int n) {
double result = Math.pow(base, n)
return (int)result;
}
// Math.pow : 거듭제곱 메서드

// Ex34
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("2진수를 입력해주세요 : ");
String str = sc.next();
int n = Integer.valueOf(str).intValue();
int result = 0;
int twoT = 1;
int[] num = new int[str.length()];
for(int i=0; i<num.length; i++) {
num[i] = n%10;
n/=10;
}
for(int x:num) {
int a = x*twoT;
result+=a;
twoT*=2;
}
System.out.println(str+"(2) = "+result+"(10)");
// Ex34
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("2진수 입력 : ");
String str = sc.next();
// Integer.parseInt(str, 2)
// ㅡ> 문자열 형태의 2진수를 정수로 변환하는 메서드(자세한건 지피티한테)
int two = Integer.parseInt(str, 2);
System.out.println(two);

👽
// Ex35
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
Random ran = new Random();
int fail = 0;
while(fail<5) {
int a = ran.nextInt(10); //
int b = ran.nextInt(10); //
int sum = a+b;
System.out.print(a+" + "+b+" = ");
int answer = sc.nextInt();
if(answer==sum) {
System.out.println("Success");
}else {
System.out.println("Fail");
fail++;
}
}
System.out.println("GAME OVER!");

👽
// Ex36
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("문장을 입력해 주세요 : ");
String str = sc.nextLine();
int[] array = new int[26];
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
char abc = str.charAt(i);
if (abc >= 'A' && abc <= 'Z') {
abc = (char) (abc + 'a' - 'A');
}
if (abc >= 'a' && abc <= 'z') {
array[abc - 'a']++;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
char abc = (char) (i + 'a');
System.out.println(abc + ":" + array[i]);
}

👽
// Ex37 팩토리얼 값 구하기
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("입력 : ");
int n = sc.nextInt();
int[] array = new int[n];
int num = n;
int mul = 1;
for(int i=0; i<array.length; i++) {
array[i] = num;
num--;
}
for(int i=0; i<array.length; i++) {
mul*=array[i];
}
System.out.print("출력 : "+mul);// Ex37
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("입력 : ");
int num = sc.nextInt();
int sum = 1;
for(int i=1; i<=num; i++) {
sum*=i;
}
System.out.print("출력 : "+sum);


https://m.blog.naver.com/PostList.naver?blogId=seo2086&categoryNo=7&logCode=0
Sui dream : 네이버 블로그
스마트인재개발원에서 빅데이터를 공부하고 있습니다.
m.blog.naver.com
https://sunnyroad.tistory.com/18
JAVA_festival 문제 풀이_1
JAVA FESTIVAL : D-1 내일은 자바 페스티벌이 열린다. 자바 페스티벌은 학원에서 진행되는 죽음(?)의 페스티벌이다. 농담이고, 부루마블 판에 주사위를 던져 나오는 숫자에 해당하는 문제를 풀면 점수
sunnyroad.tistory.com
https://sunnyroad.tistory.com/19
JAVA_festival 문제 풀이_2
지난 편에 이어 계속되는 자바 페스티벌 문제 풀이~ 문제 16. 아래와 같이 1차원의 점들이 주어졌을 때, 그 중 가장 거리가 짧은 점(index)들을 출력하시오. (단, 점들 사이의 거리는 모두 다르다.) in
sunnyroad.tistory.com
https://sunnyroad.tistory.com/20?category=1043464
JAVA_festival 보너스 문제 풀이
보너스 문제 1. Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); while (true) { System.out.print("A 입력 : "); int A = sc.nextInt(); System.out.print("B 입력 : "); int B = sc.nextInt(); if (A == 0 && B == 0) { break; }else { System.out.println("결과 : " +(A
sunnyroad.tistory.com
링크 참조
'JAVA' 카테고리의 다른 글
| DAY 14, 15 ( JDBC 코드 MVC 패턴으로 변환 실습, DAO, DTO ) (0) | 2024.06.07 |
|---|---|
| DAY 13 ( JDBC 오라클 [ 로그인, 회원정보 삭제, 조회, 수정 ] 실습 ) (0) | 2024.06.05 |
| DAY 12 ( MP3Player 실습, MVC 패턴 실습(refactoring), JDBC ) (0) | 2024.06.04 |
| DAY 11 ( 추상클래스, 인터페이스, MVC, jar 파일 추가, mp3 불러오기 실습 ) (0) | 2024.06.03 |
| DAY 10 ( 생성자, VO, 상속, 오버라이딩, 객체 casting, ArrayList ) (1) | 2024.05.31 |